Exercise Boosts Motor Skill Learning Via Changes in Brain’s Transmitters
Researchers find switch in chemical messaging is key prelude to motor skill acquisition
May 4, 2020
By Mario Aguilera
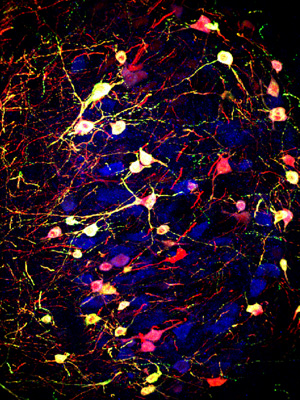
A group of midbrain neurons expressing acetylcholine (blue) are made to express another type of neurotransmitter, glutamate (yellow).
Doctors have relentlessly impressed upon us the many benefits of exercise. Energy, mood, sleep and motor skills all improve with a regular fitness regimen that includes activities such as running. This has become of particular interest in the time of the COVID-19 pandemic.
But what happens in the brain during these improved states of health? The underlying neurological changes that open the door to these benefits have been unclear.
Now, Assistant Project Scientist Hui-quan Li and Distinguished Professor Nick Spitzer of the University of California San Diego have identified key neurological modifications following sustained exercise. Comparing the brains of mice that exercised with those that did not, Li and Spitzer found that specific neurons switched their chemical signals, called neurotransmitters, following exercise, leading to improved learning for motor-skill acquisition.
“This study provides new insight into how we get good at things that require motor skills and provides information about how these skills are actually learned,” said Spitzer, the Atkinson Family Chair in the Biological Sciences Section of Neurobiology and a director of the Kavli Institute for Brain and Mind.
The study’s results are published May 4 in Nature Communications.
Spitzer’s laboratory discovered neurotransmitter switching in the adult mammalian brain and has led groundbreaking research on the ability of neurons to change their transmitter identity in response to sustained stimuli, typically leading to changes in behavior. After carrying out research that described neurotransmitter switching in depression, Spitzer and his colleagues began to turn their attention to how such switching might be involved in healthy conditions.
Li says the results underscore the importance of exercise, even at home during the current pandemic quarantine situation.
“This study shows that it’s good for the brain to add more plasticity,” said Li. “For people who would like to enhance their motor skill learning, it may be useful to do some exercise to promote this form of plasticity to benefit the brain. For example, if you hope to learn and enjoy challenging sports such as surfing or rock climbing when we’re no longer sheltering at home, it can be good to routinely run on a treadmill or maintain a yoga practice at home now.”


Videos reveal the clumsy movements of a mouse running on a wheel on the first day of exercise (left) and skilled running after a week of self-training (right).
During the new study, Li and Spitzer compared mice that completed a week’s worth of exercise on running wheels with mice that had no access to running wheels. They found that the exercised group acquired several demanding motor skills such as staying on a rotating rod or crossing a balance beam more rapidly than the non-exercised group.
When the brains of the running mice were examined, a group of neurons in the brain region known as the caudal pedunculopontine nucleus (cPPN) that regulates motor coordination was discovered to have switched neurotransmitters from acetylcholine to GABA.
To confirm their findings, the researchers used molecular tools to block the newly identified transmitter switch resulting from exercise. They found that the enhancement of motor skill learning in these mice was prevented. Based on their findings, the researchers propose a new model in which conversion of cPPN excitatory cholinergic neurons to inhibitory GABAergic neurons provides feedback control regulating motor coordination and skill learning.
The researchers say the discovery could lead to further findings where neurotransmitter switching leads to key motor skill changes. The researchers say they’d like to test ideas such as whether neurotransmitters could be deliberately switched to benefit motor skills, even without exercise. They also plan to conduct research on whether exercise similarly triggers benefits of motor skill learning in those with neurological disorders.
“We suggest that neurotransmitter switching provides the basis by which sustained running benefits motor skill learning, presenting a target for clinical treatment of movement disorders,” the authors conclude in the paper.
Says Spitzer: “With an understanding of this mechanism comes the opportunity to manipulate and to harness it for further beneficial purposes. In the injured or diseased individual, it could be a way of turning things around… to give the nervous system a further boost.”
The research was funded by grants from the Ellison Medical Foundation, the W. M. Keck Foundation, the National Institutes of Health (NS047101) and the Overland Foundation.
